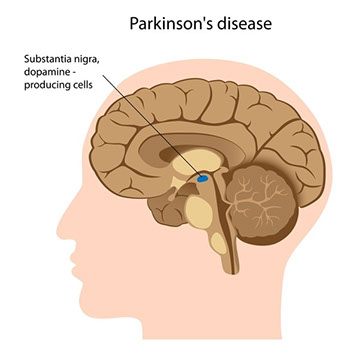
Parkinson’s is a disorder of the nervous system that affects movements and develops slowly & gradually.
The disease can, to begin with, start in a barely perceptible form with just one of the hands showing signs of trembling in a very feeble manner. Alternatively, some people also experience stiffness of the hands and gradual slowing down of movements. The disease can be passed on genetically from parent to child – but this incidence is relatively low. Exposure to certain toxins over a consistent period of time could also trigger the disease.
Symptoms of Parkinson’s disease
- Trembling of hands
- Stiffening of hands
- Slowing down of movements
- Slurred speech
- Difficulty in fine motor skills
Risk Factors of Parkinson’s disease
- Advancing Age
- Exposure to toxins
- Genetic Factors
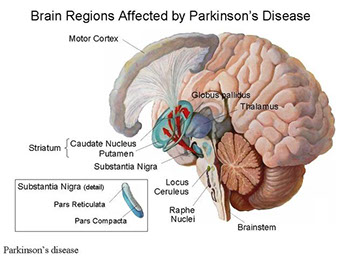
Diagnosis & Treatment of Parkinson’s disease
- Review of signs & symptoms
- Imaging tests such as MRI, PET Scans
- Blood tests
- Physical examination
- Neurological assessment
Parkinson’s disease, presently, does not have a treatment or cure. And the diagnosis itself may take a gradual process. Doctors currently seek to identify & manage the symptoms of the disease as effectively as possible to provide relief to the patient. Changes to an individual’s lifestyle may be suggested and certain physical therapies prescribed to manage conditions such as slurred speech, joint flexibility, and stiffness of muscles. Deep brain stimulation is a routinely performed procedure for the treatment of Parkinson’s with the use of a battery-operated device known as a neurostimulator.


